We have moved our location to Poughkeepsie New York – no more commuting 2 hours per day !!! New address is: Process NMR Associates, LLC, 84 Patrick Lane, Suite 115, Poughkeepsie, NY 12603-2936 Tel: (845) 240-1177
PANIC NMR Validation Group – Website, Meetings and Organization
Validation of NMR: No Need to PANIC – Workshop held February 13, 2015, La Jolla, CA, U.S.A
In conjunction with the 3rd PANIC conference in La Jolla, California, a 1-day NMR validation workshop was held that attracted approximately 80 interested participants. The agenda of the meeting is provided at this link (http://www.nmrvalidation.org/index.php/events/event-review) and registered participants can now download the presentations presented at the meeting. At the meeting it was decided to proceed with the idea of founding an organization dedicated to the development of validate NMR methods for use throughout all industry sectors.
Organizational Scope:
NMR spectroscopy provides a means to evaluate material with high compound and high material specificity. Information as to the chemical structure, stereochemistry, quantity, material composition, and material identity is encoded in the NMR spectrum. The high reproducibility of NMR spectroscopy from instrument to instrument and lab to lab makes NMR an excellent tool for material validation. Approaches to utilizing NMR as a material validation tool include using (1) targeted approaches, the identification and quantification of specific components, and (2) non-targeted approaches, the use of chemometric methods to evaluate the spectrum as a whole. Efforts to increase the number and the speed of validated NMR methods are underway. This promises to move NMR technology from R&D to a mainstream analytical tool for production leading to high quality product assessment.
Quantitative NMR spectroscopy (qNMR) provides the most universally applicable form of direct purity determination without the need for reference materials of analytes or the calculation of response factors, with the only requirement being the exhibition of suitable NMR spectral properties. Due to recent advances in the technical development of NMR instruments, such as acquisition electronics and probe design, detection limits of components in liquid mixtures have been improved into the lower ppm range (approx. 5–10 ppm amount of substance).
The development of validated procedures and qualified standards will give users the tools to routinely exploit qNMR and enable them to speed up analytical method development, with the added advantage of reducing the time and financial burden of multiple analytical testing.
Over the last few years a number of efforts have been made to include NMR in routine testing and analysis – especially in regulated fields such as those operating under GMP or GLP guidelines. Unfortunately it has been observed that approval authorities, standard method organizations, and auditors prefer to take analytical routes derived from classical chromatographic methods. Since NMR represents a direct comparison analysis method such decisions clearly fail to take advantage of the benefits that NMR can provide.
The PANIC validation group proposes to become a driving force in getting NMR methods validated, publicized, and supported by documentation and qualified standards. The organization will also provide a mechanism for repeatability/reproducibility assessment of NMR methods as well as the round-robin accreditation of NMR labs. We aim to proactively promote the technology and improve its acceptance by the analytical community across all industry sectors.
What we want:
- Identify a network of NMR people concerned with validation that can ultimately assist each other through the validation process.
- Harmonize the terminology and a standard approach for NMR validations.
- Position the guidelines produced by consensus of the NMR community so that accreditation agencies can use this process.
It is expected that there will be an annual 1-day meeting in conjunction with future PANIC conferences. A website has been been created as an organizational repository. The website can be found here: http://www.nmrvalidation.org/index.php and details of future events and, eventually, contact information will be provided.
Polyalphaolefin Hydrogenation – Residual Olefin Analysis – 1H NMR versus Bromine Number
1H NMR is an excellent tool for monitoring the residual olefin content of polymers after hydrogenation reactions. The fact that the olefin fall in a unique region of the spectrum means that it is a straightforward measurement to quantify the %H present as olefin or to correlate that olefin content with other analyses such as bromine number. Here is an example of a polyalphaolefin residual olefin analysis. The olefin proton content (%H) was plotted against bromine number values obtained on each of the samples. A linear correlation was obtain but two different correlations were observed that were dependent on the viscosity index of the polyalphaolefin being analyzed. Figure 1 shows the 1H NMR spectra obtained on neat samples on a Picospin-80 spectrometer operating at 82.3 MHz. The methyl and methlene protons of the polymer backbone are plainly seen and the olefin and alpha-olefin protons are observed.
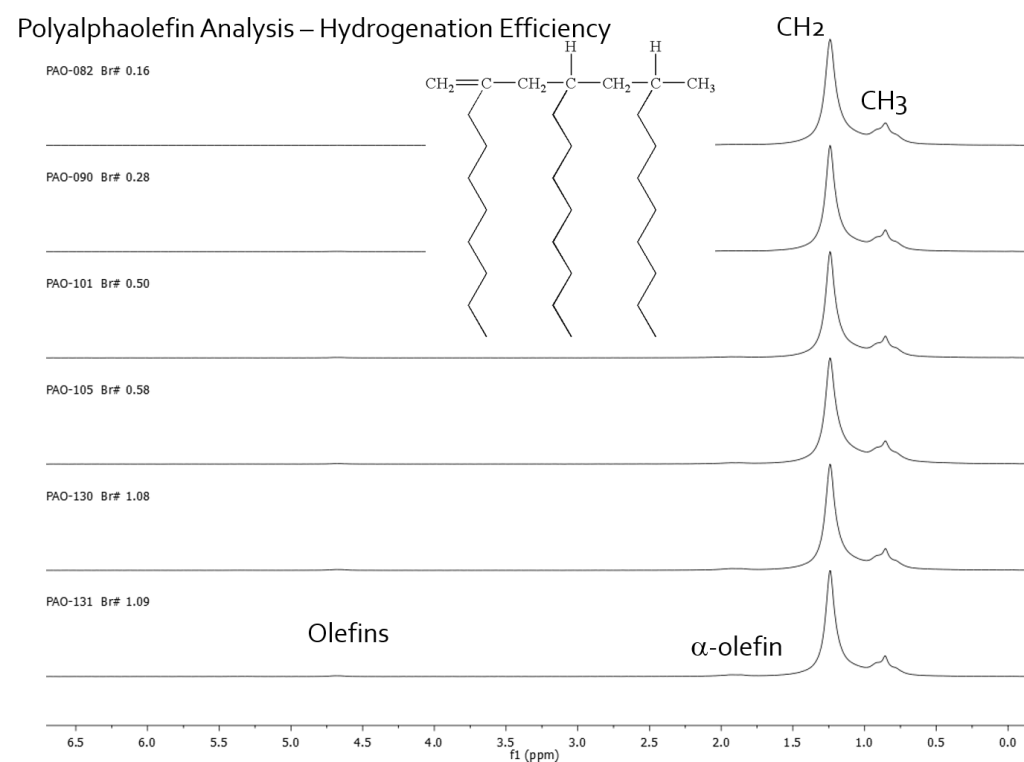
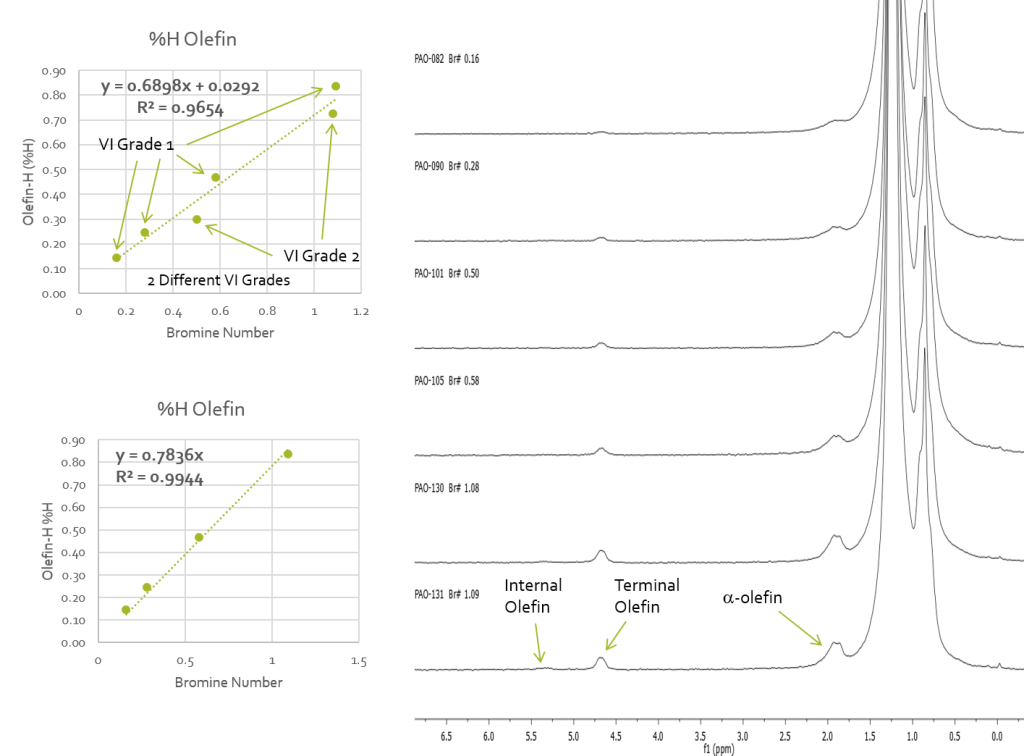
Figure 2 shows the linear correlation between %H olefin and bromine number with the two correlations caused by different VI grade being indicated. The analysis shows that for the two viscosity grades the grade can be identified from the linear correlation that the data falls onto and the %H olefins content can directly yield the bromine number. This NMR method provides an alternative to the following ASTM standards: D1159 Test Method for Bromine Numbers of Petroleum Distillates and Commercial Aliphatic Olefins by Electrometric Titration D1491 Test Method for Test for Bromine Index of Aromatic Hydrocarbons by Potentiometric Titration D1492 Standard Test Method for Bromine Index of Aromatic Hydrocarbons by Coulometric Titration D2710 Test Method for Bromine Index of Petroleum Hydrocarbons by Electrometric Titration D5776 Test Method for Bromine Index of Aromatic Hydrocarbons by Electrometric Titration
Residual Catalytic Cracker – Heavy Petroleum Feedstream Properties from 1H NMR at 43 MHz
Back in October we presented a talk at Gulf Coast Conference that concerned the prediction of the chemical and physical properties of heavy petroleum feeds being converted to higher value product in a residual catalytic cracker (RCC). Over the years we have analyzed these materials by 300 and 60 MHz NMR and obtained good PLS-regression models that can adequately predict properties for real-time process control and optimization in a petroleum refinery. With the advent of a large number of new benchtop NMR systems we have been convincing ourselves that these types of analyses can be performed by systems such as the Magritek Spinsolve 43 MHz. We ran a series of samples that had been sitting around our lab for 15 years by dissolving them at about 50 volume% in a 50/50 CDCl3/CS2 solvent system. For each sample we had laboratory test data for a number of chemical and physical properties of interest to process engineers. We regressed the lab data variability against the variability in the Magritek 43MHz 1H NMR spectra and obtained cross-validated PLS models. The presentation material is given here at this link – Gulf Conference Presentation – 43 MHz RCC Feedstream Regression Models
From Atoms to Flavour: The Chemistry of Beer
Adam DiCaprio (ex PNA) gave an excellent Science Cafe Talk under the auspices of the ACS North Carolina Section at the Busy Bee Cafe in downtown Raleigh on December 2, 2014. CHanging gears from his previous talks he centered the discussion on malt and hop chemistry as well as an start-to-finish NMR analysis of production runs of a bottled commercial tavern ale. If you are interested in having Adam give a detailed chemistry seminar on beer at your section meetings please contact him directly at adam@process-nmr.com.
A PDF version of his talk is available here …. ACS Science Cafe Talk – Dicaprio – Busy Bee Cafe – Raleigh NC – 12-2-14